Oxygen Absorbers: Measuring Volume of Oxygen

You will need to know the volume of oxygen in your container so that you can determine what size of oxygen absorber to use. Oxygen is measured in cubic centimeters (cc). The sizes of our oxygen absorbers correspond to the amount of oxygen they absorb. For example, a 300 cc oxygen absorber will absorb 300 cc of oxygen.
The table below indicates how many cc's of oxygen are contained in the more common sizes of food storage containers.
| Container Type | Volume in Empty Container |
|---|---|
| #10 can | 3,980 cc |
| 5 gallon plastic pail | 18,942 cc |
| 6 gallon plastic pail | 22,730.4 cc |
Oxygen absorbers are rated by their capacity to absorb oxygen as measured in cubic centimeters (cc).
There are two key elements to keep in mind when determining what size of oxygen absorber to use:
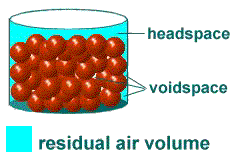
Headspace
As in the table above, a #10 can has a volume of 3,980 cc. If you fill this can to 90% of its volume, you will have 398 cubic centimeters of headspace. Because air is 21.0% oxygen, this headspace will contain 81.6 cubic centimeters of oxygen (0.21 x 398 = 81.6).
Voidspace
If a five-gallon bucket were filled with children's marbles, the spaces in between the marbles (void spaces and head space) would represent 38% of the volume of the five-gallon pail ( 0.38 x 18,942 cc = 7,197.96 cc residual air volume ). Of this number, 21.0% is oxygen.
(x) cc Headspace + (x) cc Voidspace = Residual Air Volume
In order to determine how much oxygen absorbing capacity you require, we must determine the residual air volume. Here is a fairly simple way of determining this quantity, using weight and volume measurements.
- Determine the volume of your container. Use the table above for common container types. Or use the tables below
- Weigh the food product and convert this weight to grams. (See conversion table below.) To be completely accurate, make sure you subtract the weight of the container to get the net weight of the food.
- Subtract the cubic centimeter volume found in Step 1 above from the gram weight found in Step 2 above to determine the headspace and voidspace, or residual air volume. (This will be a measurement in cubic centimeters)
- Finally, as there is approximately 21.0% oxygen in air, multiply the residual air volume found in Step 3 above by .21 to get the cubic centimeter volume of oxygen in your product container.
Example:
We want to know what size oxygen absorber to use for a 5 gallon bucket of rice.
- We determine from the table above that there are 18,942 cubic centimeters in a 5 gallon plastic bucket.
- The rice weighs 35 pounds which converts to 15,876 grams.
- 18,942 (cc) container volume - 15,876 (g) rice = 3,066 cc residual air volume.
- 3,066 (cc) residual air volume x .21 (oxygen fraction in air) = 628.53 cc oxygen volume.
- Since the size of oxygen absorbers are rated and named according to the amount of oxygen they absorb, we know that a 750 cc oxygen absorber will be sufficient for this bucket of rice.
If your container is a regular shape such as in the diagram below, use the formula which follows:
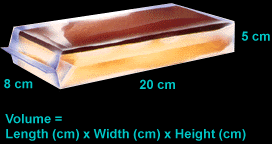

NOTE: one milliliter (ml) = one cubic centimeter (cc)
If your container is an irregular shape, such as a flexible mylar® bag, the oxygen volume can be determined by doing the following:

For purpose of this calculation, we are going to assume that the specific gravity of the product has a value of 1.
- Fill a vessel with water. Place your product container (containing the food) into the vessel and let the water overflow.
- Remove your container from the vessel.
- Measure how much water it takes to fill the vessel back up with water. The water is measured in milliliters (ml). There are 29.57 ml in one fluid ounce.
- Measure the weight of the product container in grams (g). There are 28.35 grams in an ounce.
The formula for this is as follows:

NOTE: one milliliter (ml) = one cubic centimeter (cc)
In the example above, the oxygen in the container is 30 ml. Therefore, an oxygen absorber will have to be at least 30 cc. Our 50 cc oxygen absorber will be more than sufficient.
Specific Gravity
Relative density (measure of the density of a substance compared with that of a standard) when the standard substance is pure water.
| MEASUREMENT CONVERSION TABLE | ||
|---|---|---|
| To Convert: | To: | Multiply by: |
| inches | centimeters | 2.54 |
| square inches | square centimeters | 6.54 |
| cubic inches | cubic centimeters | 16.387 |
| fluid ounces | milliliters | 29.57 |
| ounces (weight) | grams | 28.35 |
